0. 为什么会有这篇博客
我在学习 EF Core 时,经常看到示例代码中在配置实体时对 string 类型的属性调用 IsUnicode() 方法。我不理解,所以我先学习了一些 ASCII 、Unicode、UTF-8 等知识,不了解的朋友可以看一下我这篇文章:彻底理解 ASCII Unicode UTF-8 UTF-32 是什么以及区别与联系 https://blog.kitlau.dev/posts/thoroughly-understand-ascii-unicode-utf-8-utf-32/,然后我打算试验一下这个方法。
1. 准备工作
您可以直接下载我的代码,具体运行方法请阅读代码中的 README.md 文件。
代码地址:https://github.com/Kit086/kit.demos/tree/main/EFCore/IsUnicode
如果因为网络原因下不到代码,可以参考下面我的步骤来写。当然也可以什么都不做直接看我的结论。
我计划在 MariaDB 和 MS SQL Server 测试该配置方法。MariaDB 是我一直在用的免费关系型数据库,MS SQL Server 是大部分使用 .NET 技术的公司选用的关系型数据库。
创建项目,引入包
首先创建一个控制台应用,引入三个 NuGet 包:
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DesignPomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySqlMicrosoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
创建实体类
创建三个实体类,一个默认配置,一个配置为 IsUnicode()(默认参数为 true),一个配置为 IsUnicode(false)。
默认配置 Person.cs:
public class Person
{
public long Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Person: Id: {Id}, Name: {Name}, Name.Length: {Name.Length}";
}
}
public class PersonConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Person>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Person> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(x => x.Id);
builder.Property(x => x.Name)
.HasMaxLength(128)
.IsRequired();
}
}
配置为 IsUnicode() PersonWithUnicodeName.cs:
public class PersonWithUnicodeName
{
public long Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
public override string ToString()
{
return $"PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: {Id}, Name: {Name}, Name.Length: {Name.Length}";
}
}
public class PersonWithUnicodeNameConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<PersonWithUnicodeName>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<PersonWithUnicodeName> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(x => x.Id);
builder.Property(x => x.Name)
.IsUnicode()
.HasMaxLength(128)
.IsRequired();
}
}
配置为 IsUnicode(false) PersonWithoutUnicodeName.cs:
public class PersonWithoutUnicodeName
{
public long Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
public override string ToString()
{
return $"PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: {Id}, Name: {Name}, Name.Length: {Name.Length}";
}
}
public class PersonWithoutUnicodeNameConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<PersonWithoutUnicodeName>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<PersonWithoutUnicodeName> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(x => x.Id);
builder.Property(x => x.Name)
.IsUnicode(false)
.HasMaxLength(128)
.IsRequired();
}
}
创建数据库上下文
AppDbContext.cs:
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Person> Persons { get; set; } = null!;
public DbSet<PersonWithUnicodeName> PersonWithUnicodeNames { get; set; } = null!;
public DbSet<PersonWithoutUnicodeName> PersonWithoutUnicodeNames { get; set; } = null!;
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
#region MariaDB Configuration
// optionsBuilder.UseMySql("server=localhost;port=3306;database=is_unicode_test;user=root;password=password;",
// new MariaDbServerVersion(new Version(10, 6)));
#endregion
#region MSSQL Configuration
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=localhost;Database=IsUnicodeTest;User Id=sa;Password=Password01!;");
#endregion
optionsBuilder.LogTo(Console.WriteLine);
base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder);
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
public async Task SeedAsync()
{
if (!this.Persons.Any())
{
this.Persons.Add(new Person
{
Name = "Zhang Three"
});
this.Persons.Add(new Person
{
Name = "李四"
});
this.Persons.Add(new Person
{
Name = "王😿"
});
}
if (!this.PersonWithUnicodeNames.Any())
{
this.PersonWithUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithUnicodeName
{
Name = "Zhang Three"
});
this.PersonWithUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithUnicodeName
{
Name = "李四"
});
this.PersonWithUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithUnicodeName
{
Name = "王😿"
});
}
if (!this.PersonWithoutUnicodeNames.Any())
{
this.PersonWithoutUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithoutUnicodeName
{
Name = "Zhang Three"
});
this.PersonWithoutUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithoutUnicodeName
{
Name = "李四"
});
this.PersonWithoutUnicodeNames.Add(new PersonWithoutUnicodeName
{
Name = "王😿"
});
}
await this.SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
OnConfiguring() 方法中有对 MariaDB 和 MSSQL 的配置,假如您想要使用 MariaDB 进行测试,解除 MariaDB Configuration region 中配置代码的注释,然后注释掉 MSSQL Configuration region 中对 MSSQL 配置的代码。
将 OnConfiguring() 方法中的 MariaDB 或 MS SQL Server 的连接字符串改为您自己的测试数据库的连接字符串。
该类中还有一个 SeedAsync() 方法,用于添加种子数据。我自定义了三个实体各三个种子数据,Name 字段覆盖了纯英文字符的 Zhang Three,纯中文字符的 李四,以及包含 emoji 的 王😿。
编写 Program.cs
Program.cs:
await using AppDbContext dbContext = new AppDbContext();
await dbContext.SeedAsync();
var personList = await dbContext.Persons.ToListAsync();
var personWithUnicodeNameList = await dbContext.PersonWithUnicodeNames.ToListAsync();
var personWithoutUnicodeNameList = await dbContext.PersonWithoutUnicodeNames.ToListAsync();
// Console.OutputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
personList.ForEach(p => Console.WriteLine(p.ToString()));
personWithUnicodeNameList.ForEach(pwu => Console.WriteLine(pwu.ToString()));
personWithoutUnicodeNameList.ForEach(pwtu => Console.WriteLine(pwtu.ToString()));
添加迁移及生成数据库
在修改好 AppDbContext.cs 中的 OnConfiguring() 方法中的配置后,可以运行以下步骤添加迁移:
- cd 到含有 IsUnicode.csproj 文件的目录下,
- 删除 Migrations_MSSQL 和 Migrations_MariaDB 两个目录及其中的内容。因为这是我本地的 Migration 文件
- 运行命令
dotnet ef migrations add Init - 运行命令
dotnet ef database update命令,生成数据库
2. 测试程序,观察 IsUnicode() 对程序的影响
MariaDB
我在使用 MariaDB 的配置时,添加完迁移后,查看生成的迁移文件的关键代码,特别是 Up() 方法:
protected override void Up(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.AlterDatabase()
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4");
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "Persons",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:ValueGenerationStrategy", MySqlValueGenerationStrategy.IdentityColumn),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "varchar(128)", maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4")
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_Persons", x => x.Id);
})
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4");
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "PersonWithoutUnicodeNames",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:ValueGenerationStrategy", MySqlValueGenerationStrategy.IdentityColumn),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "varchar(128)", unicode: false, maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4")
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_PersonWithoutUnicodeNames", x => x.Id);
})
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4");
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "PersonWithUnicodeNames",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:ValueGenerationStrategy", MySqlValueGenerationStrategy.IdentityColumn),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "varchar(128)", maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4")
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_PersonWithUnicodeNames", x => x.Id);
})
.Annotation("MySql:CharSet", "utf8mb4");
}
可以看到整个数据库的字符集被设置为了 utf8mb4,三张表的字符集也默认被设置为 utf8mb4。三个表的 Name 列数据类型都为 varchar(128),PersonWithoutUnicodeNames 表的 Name 列多了 unicode: false,Persons 表和 PersonWithUnicodeNames 表没什么区别,看来使用 Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql 这个包时,默认的对 string 的配置就是 IsUnicode(true)。
我记录下了控制台日志中输出的创建数据库的关键代码:
Build started...
Build succeeded.
info: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.320 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (9ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE DATABASE `is_unicode_test`;
info: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.653 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (2ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
ALTER DATABASE CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
info: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.687 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (33ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE `Persons` (
`Id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT `PK_Persons` PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) CHARACTER SET=utf8mb4;
info: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.720 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (32ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE `PersonWithoutUnicodeNames` (
`Id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT `PK_PersonWithoutUnicodeNames` PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) CHARACTER SET=utf8mb4;
info: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.754 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (32ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE `PersonWithUnicodeNames` (
`Id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT `PK_PersonWithUnicodeNames` PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) CHARACTER SET=utf8mb4;
dbug: 2022/8/5 23:47:42.764 CoreEventId.ContextDisposed[10407] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Infrastructure)
'AppDbContext' disposed.
Done.
创建三张表的 SQL 脚本除了表名外没有任何区别,即使 PersonWithoutUnicodeNames 表的 Name 属性我们配置了 IsUnicode(false),生成的迁移文件中也有了体现:unicode: false,但生成的 SQL 脚本中,依然是 varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 NOT NULL,,字符集还是 utf8mb4。
是不是这个配置只在读数据库后对读出来的对象有影响?运行程序测试一下。输出结果:
Person: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
Person: Id: 2, Name: 李四, Name.Length: 2
Person: Id: 3, Name: 王😿, Name.Length: 3
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 2, Name: 李四, Name.Length: 2
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 3, Name: 王😿, Name.Length: 3
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 2, Name: 李四, Name.Length: 2
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 3, Name: 王😿, Name.Length: 3
没有任何影响。我们可以得出结论,由于默认字符集为 utf8mb4,IsUnicode() 这个配置对 MariaDB 没有任何影响。
MS SQL Server
看一下生成的迁移文件的关键代码:
protected override void Up(MigrationBuilder migrationBuilder)
{
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "Persons",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("SqlServer:Identity", "1, 1"),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "nvarchar(128)", maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_Persons", x => x.Id);
});
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "PersonWithoutUnicodeNames",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("SqlServer:Identity", "1, 1"),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "varchar(128)", unicode: false, maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_PersonWithoutUnicodeNames", x => x.Id);
});
migrationBuilder.CreateTable(
name: "PersonWithUnicodeNames",
columns: table => new
{
Id = table.Column<long>(type: "bigint", nullable: false)
.Annotation("SqlServer:Identity", "1, 1"),
Name = table.Column<string>(type: "nvarchar(128)", maxLength: 128, nullable: false)
},
constraints: table =>
{
table.PrimaryKey("PK_PersonWithUnicodeNames", x => x.Id);
});
}
Persons 和 PersonWithUnicodeNames 表的 Name 列数据类型都为 nvarchar(128),而配置了 IsUnicode(false) 的 PersonWithoutUnicodeNames 表的 Name 列的数据类型为 varchar(128),还多了 unicode: false。看起来似乎影响比较大。
我记录下了控制台日志中输出的创建数据库的关键代码:
Build started...
Build succeeded.
info: 2022/8/6 00:26:00.385 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (272ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='60']
CREATE DATABASE [IsUnicodeTest];
info: 2022/8/6 00:26:00.746 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (3ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE [Persons] (
[Id] bigint NOT NULL IDENTITY,
[Name] nvarchar(128) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Persons] PRIMARY KEY ([Id])
);
info: 2022/8/6 00:26:00.750 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (3ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE [PersonWithoutUnicodeNames] (
[Id] bigint NOT NULL IDENTITY,
[Name] varchar(128) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_PersonWithoutUnicodeNames] PRIMARY KEY ([Id])
);
info: 2022/8/6 00:26:00.754 RelationalEventId.CommandExecuted[20101] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command)
Executed DbCommand (3ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE [PersonWithUnicodeNames] (
[Id] bigint NOT NULL IDENTITY,
[Name] nvarchar(128) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_PersonWithUnicodeNames] PRIMARY KEY ([Id])
);
dbug: 2022/8/6 00:26:00.771 CoreEventId.ContextDisposed[10407] (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Infrastructure)
'AppDbContext' disposed.
Done.
唯一的区别是 PersonWithoutUnicodeNames 表的 Name 列的数据类型为 varchar(128)。另外两个表为 nvarchar(128)。
运行一下程序,看一下结果:
Person: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
Person: Id: 2, Name: 李四, Name.Length: 2
Person: Id: 3, Name: 王😿, Name.Length: 3
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 2, Name: 李四, Name.Length: 2
PersonWithUnicodeName: Id: 3, Name: 王😿, Name.Length: 3
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 1, Name: Zhang Three, Name.Length: 11
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 2, Name: ??, Name.Length: 2
PersonWithoutUnicodeName: Id: 3, Name: ???, Name.Length: 3
PersonWithoutUnicodeName 的 Name(varchar(128))中的中文与 emoji 均无法正常输出,而 Person 与 PersonWithUnicodeName 的 Name(nvarchar(128))中的中文与 emoji 均能正常输出,所以可以排除 Terminal 或者操作系统这些外部原因,问题确实出在 IsUnicode(false) 这个配置上。
3. IsUnicode() 的作用
通过实验,我们发现 IsUnicode() 对 MariaDB 没什么用,对 MSSQL Server 则会改变 C# string 类型的属性在数据库中的数据类型。当不使用 IsUnicode() 或配置为 IsUnicode(true) 时,生成的数据库表中对应 string 字段的数据类型为 nvarchar,而配置 IsUnicode(false) 时则为 varchar。
4. 何时使用 IsUnicode()
使用 MariaDB 时用不用都无所谓了。
使用 MSSQL Server 时,我认为,当我们确定一个 string 类型的属性是 **ASCII 安全(ASCII SAFE)**的时候,即这个属性的值只会包含数字、英文字母和英文符号时,可以为它配置 IsUnicode(false),这样它在数据库中就是 varchar 类型。但如果你不确定,最好还是保持默认。如果你不放心,或者想让团队的其他开发成员能够明明白白的知道每个 string 类型的属性到底是 varchar 还是 nvarchar,可以全部都显式配置。
对 ASCII 和 Unicode、UTF-8 犯迷糊?别担心,这是正常的,可以看一下我这篇文章:彻底理解 ASCII Unicode UTF-8 UTF-32 是什么以及区别与联系 https://blog.kitlau.dev/posts/thoroughly-understand-ascii-unicode-utf-8-utf-32/,包会。
5. 我的经验
对于 ASCII 安全的字符串来说,
nvarchar要比varchar多占 1 倍的存储空间,而且还要考虑性能的影响。我曾经维护过一个单表二十多亿条数据的项目,因为客户端开发的朋友不小心把 5 分钟调一次接口写成了 5 毫秒调一次接口。该项目是古老的 .NET Framework 项目,没有使用什么限流措施。在我之前的不知道哪位开发人员很大方的给这张表全用了
nvarchar,然后他润了我被 DBA 怼了......假设你确实有一张表要存上千万甚至上亿数据,把 ASCII 安全的列设置IsUnicode(false)是有必要的。可能巨有钱的巨硬(微软)觉得存储空间不值钱,但是在内存中 MS SQL Server 是把数据存到一个个 8k 大小的数据页中,数据列越宽,在需要再次转到磁盘之前,同一个数据页中能存的数据就越少。从磁盘读取总是比从内存读取慢,慢多少? 学过计算机组成原理的朋友应该都有数,当然这也取决于特定服务器或磁盘的 I/O 成本等。
对数据库如何存储数据有疑惑的朋友可以看一下我的这两篇文章:
- 【译】SQL 索引是如何工作的 https://blog.kitlau.dev/posts/how-do-sql-indexes-work/
- 【译】数据是如何存储在 SQL 数据库中 https://blog.kitlau.dev/posts/how-is-data-stored-in-sql-database/
但是如果你不确定你的字符串是 ASCII 安全的,最好使用默认的配置,或者显式配置
IsUnicode()或IsUnicode(true),磁盘很便宜,内存只要不是你自己出钱也都很便宜,不要因为刷 leetcode 养成的极度性能和存储空间洁癖而因小失大(我已经被 leetcode 虐爆了,I am toooooo vegetable,我的级别还用不上算法,我现在不刷 leetcode 了,我刷 let's cook: https://github.com/Anduin2017/HowToCook,我觉得当厨师比较有钱途)。
6. 一些容易犯错的情况
- 让你设计一个存储 URL 的字段,你会不会直接就
IsUnicode(false)了?我暂时不知道你怎么想,但是这里有一位从 1988 年就不再写代码了,2009 年又重拾写代码的骨灰级程序猿,《Entity Framework Core in Action》的作者,是很顶级的 .NET 开发者了,他是想用varchar来存 URL:
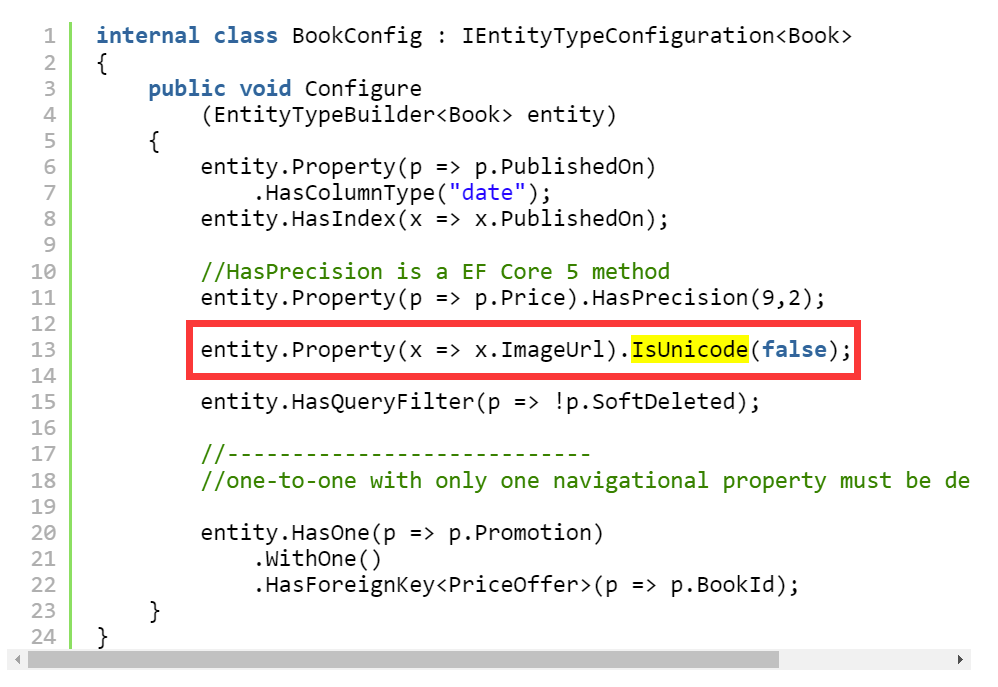 |
|---|
| 图 1 |
他还给所有属性名为 Url 结尾的属性都设置了 IsUnicode(false):
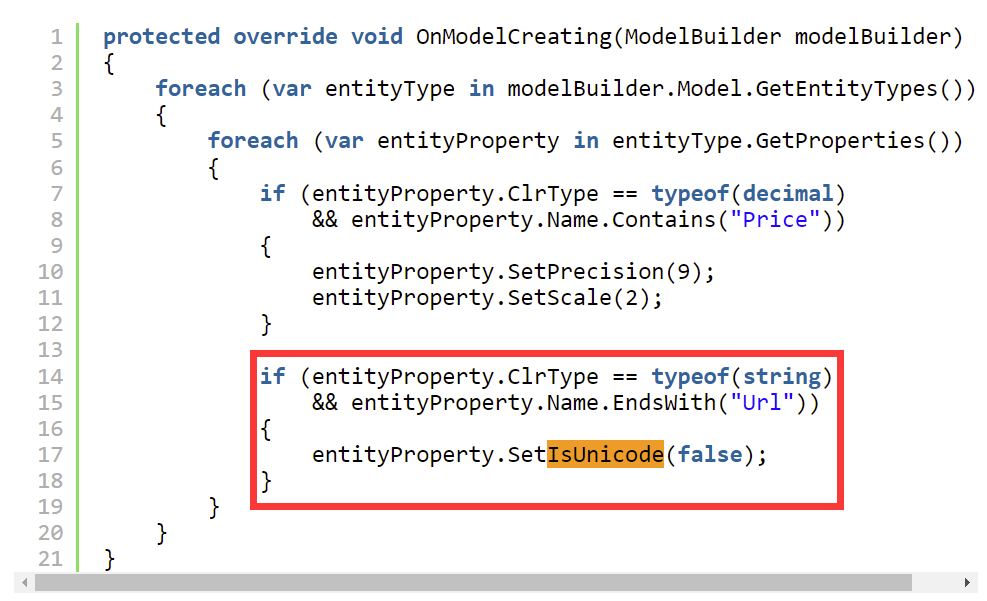 |
|---|
| 图 2 |
但是他这次翻车了。当你用 URL 访问 Web 服务器的时候,确实不能包含 Unicode 字符,这是因为你在浏览器中使用 ASCII 不安全的 URL 字符串时,浏览器会帮你处理。但是数据库有可能保存用户录入的数据,用户可能录入这种 URL:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/中文
- http://newspaper.annahar.com/article/121638-معرض–جوزف-حرب-في-غاليري-جانين-ربيز-لوحاته-الجدية-تبحث-وتكتشف-وتفرض-الاحترام
所以最好不要配置 URL 为 varchar。
这种高手都有翻车的时候,你我又有什么理由在使用 IsUnicode(false) 前不深思熟虑仔细斟酌呢?
顺带一提,《Entity Framework Core in Action》是一本很不错的书,不止教 EF Core,我实在是没耐心,仅仅看了第一部分,但是已经见识了很多闻所未闻的代码模式和技巧了。
- 不要低估了你的用户,就算你的用户全用英语,他们评论的内容,也极有可能添加各种 emoji。我就常常在评论中加入各种字符,中文日语希腊字母阿拉伯语 emoji 以及各种鬼画符,不要让用户把你的系统搞崩了。
7. Unicode Attribute
EF Core 6 中引入了新玩意儿:Unicode Attribute。你也可以这样配置 IsUnicode(false) 的属性了:
[Unicode(false)]
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
总结
软件开发处处是坑,即使 ASP.NET Core 和 EntityFramework Core 这种成熟的库也很难做到上手即用,还是要多学多看。欢迎关注我的博客,我会常常分享一些其它博主并不太留意,却很关键的计算机基础知识和编程知识。